Poster (P61)
Bonding of metal nanoparticles with DNA Base (Adenine) in gas and solvent phase using density functional theory
Sumana Gop, Ranjan Sutradhar, Sumana Chakraborty, T. P. Sinha
Department of Physics, Bose Institute, 93/1 A P C Road, Kolkata 700009, India
Abstract
Nanoparticles (Nps) are being used in many application related areas in today`s life. They have various potential application in everywhere due to their unique properties, among them most important application is in medical treatment [1]. Nps can be used as optical imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and also as drug carrier in diagnostic field. Nowadays Nps are being used successfully in Cancer treatment. Various platinum, palladium and Ruthenium based drugs have been developed for Cancer treatment [2, 3]. Zn, Ti, Fe etc transition metals based structures are used as drug carrier [4]. DNA is the fundamental unit of life containing four bases Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) And Cytosine (C). The interaction of transition metals and metal complexes with DNA bases influence the functional and stabilization properties of the bases. Therefore binding of metal nanoparticles to nucleic acid has been the subject of study for many years. Non-covalent interaction of Ag, Cu, Au, with DNA bases have been studied previously [5, 6]. Still there is enough scope to discuss about the covalent interaction of metal nanoparticles with the DNA bases and also about the various possible geometrical structures and their stability.
To fulfill our aim we have initially started with the Watson-Crick structure of purine base Adenine (A) to interact with several transition metals such as Pt, Pd, Ru etc. The interaction of various nanoparticles with different site of Adenine has been observed in our study. Adenine and metal mediated adenine complexes have been developed with Gaussview 5.0.8. All theoretical calculations are carried out using Gaussian 09 package of computational chemistry programs. The geometry optimization and stabilities have been determined at the Density functional theory (DFT) level with Cam-B3LYP/LanL2DZ (Becke`s three parameters hybrid method with Lee-Yang-Parr exchange correlation functional using the coulomb attenuating model) and M062X/LanL2DZ model in gas phase as well as solvent phase [7]. The interaction of solute solvent has been carried out by conductor like polarisable continuum model (CPCM) with water and acetone. Theoretical analysis on molecular structures, energetic stabilities and spectroscopic properties conductive properties of adenine-nanomaterial complexes is in progress.
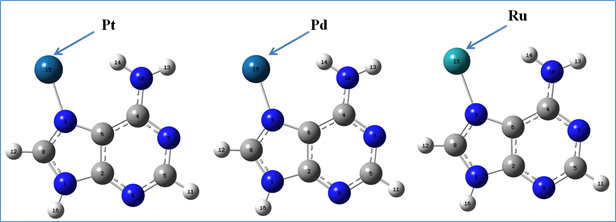
References:
[1] W. Qiao et al. Journal of Nanomaterails 2010 (2010) 796303
[2] J. Reedijk Curr Opin Chem Biol 3 (1999) 236-240
[3] M. P. M. Marques ISRN Spectroscopy 2013 (2012) 1-29
[4] S. Onsori, E. Alipour J.mol.liq 256 (2018) 558-564
[5] K-H .Cho et al. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society 29 (2008) 1
[6] K-H Cho et al. Journal of Molecular Structure 738 (2005) 9-14.
[7] M. J. Frisch et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, (2009).